A prosthetic arm that decodes phantom limb movements
About 75% of amputees exhibit mobility of their phantom limb. Using this information, in collaboration with physicians1 , researchers from CNRS and Aix-Marseille University have developed a prototype capable of detecting these movements and activating a prosthetic arm. The prosthesis does not require any surgery and patients do not need training. The results are published on November 29, 2018 in Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.
- 1Institut des Systèmes Intelligents et Robotiques (CNRS/Sorbonne Université), Institut des Sciences du Mouvements – Etienne-Jules Marey (CNRS/Aix-Marseille Université) et Institut Régional de Médecine Physique et de Réadaptation (UGECAM Nord-Est)
Most amputees feel sensations where their missing limb used to be, hence the name “phantom limb.” In a previous study2 , researchers had shown that more than 75% of amputees can voluntarily move their phantom limb. The execution of these “phantom” movements, such as for instance finger pinching, the hand making a fist, or the wrist rotating or flexing, are always associated with specific muscle contractions in the stump. In people with an upper arm amputation, these contractions concern muscle groups that are not connected with the joints used before the amputation, as if muscle reinnervation had spontaneously occurred, without surgery.
The team of researchers has developed a natural approach of prosthesis control that exploits this phenomenon. For the prototype, the researchers created algorithms capable of recognizing muscle activity generated by mobilization of the phantom limb and reproduction of the detected movement by the prosthesis: intuitive control, without training or surgery.
In the tests, two transhumeral amputees used this type of control to act with a prosthesis not worn but placed near their arm stump. The results were very encouraging. They showed that the participants could control the prosthesis and achieve the task after only a few minutes of familiarization with the system, despite long action periods. This research is very promising, since arm amputees often have difficulty in controlling their prostheses effectively, to a point that many give it up.
The researchers are continuing their work by moving on to tests on prostheses being worn, while also contributing to increasing knowledge about the phenomenon of the phantom limb, whose mechanisms are not yet properly understood. These scientists have also shown the need to reconsider the phenomenon of phantom limbs, generally taboo, often attributed to mourning the lost limb, and mainly considered from the angle of pain.
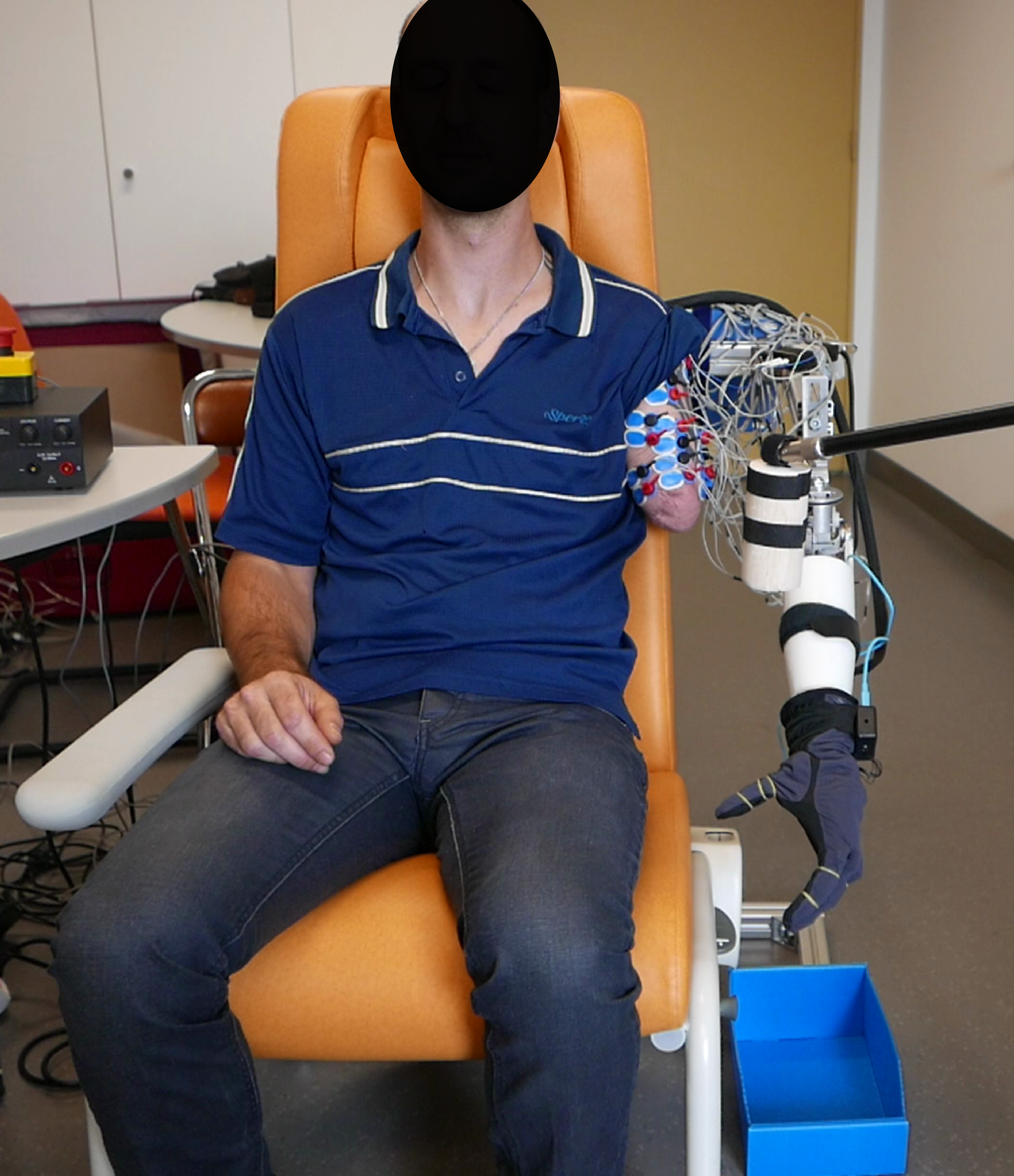
© N. Jarrassé 2018

© E. Montalivet 2018.
- 2Characteristics of phantom upper limb mobility encourage phantom-mobility-based prosthesis control. Amélie Touillet, Laetitia Peultier-Celli, Caroline Nicol, Nathanaël Jarrassé, Isabelle Loiret, Noël Martinet, Jean Paysant & Jozina B. de Graaf. Scientific Reports, Vol 8, Iss 1, Pp 1-10 (2018) DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-33643-0
Phantom-mobility-based prosthesis control in transhumeral amputees without surgical reinnervation: a preliminary study. N. Jarrassé, E. De Montalivet, F. Richer, C. Nicol, A. Touillet, N. Martinet, J. Paysant and J.B. De Graaf. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, November 29, 2018. DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00164